
Pregnancy is a physiological period in a woman's life during which a new life develops in her body. It is a unique and complex process that begins with fertilization and ends with birth.
Fertilization is the process by which a man's sperm cell unites with a woman's egg. After fertilization, the ovum begins to divide and form into an embryo. During the first two weeks after fertilization, important stages of embryonic development occur, including the initial formation of organ systems.
Approximately 10-14 days after fertilization, the embryo implants in the wall of the woman's uterus - this is called implantation. Implantation marks the beginning when the uterus begins to form the placenta, a special organ that supplies food and oxygen to the growing fetus. The placenta also plays an important role in the production of hormones that are needed to maintain pregnancy.
After the first 8 weeks after fertilization, when most of the important organs and systems begin to form, the embryo becomes a fetus. The fetus continues to grow until birth, and the pregnancy process is regulated by various hormones, including hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), progesterone, and estrogen.
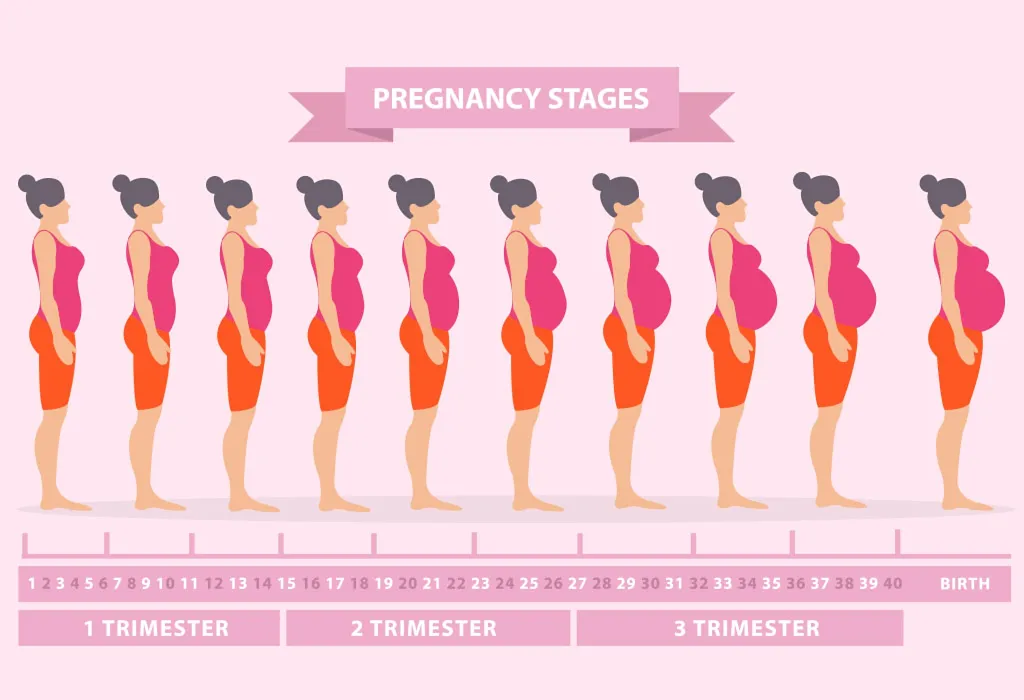
The duration of pregnancy from the start of the last menstrual period to the birth is usually about 40 weeks. This period is divided into three trimesters, each about 13-14 weeks long, which represent different stages of development.
Pregnancy is an important period in the life of both a woman and her baby. This is the period when the woman's body adapts to the new condition and prepares for childbirth, and the baby improves its growth and development in the mother's womb.
Pregnancy and its stages
Pregnancy is usually divided into three stages called trimesters. Each of them involves certain developmental stages and physiological changes for both mother and baby.
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12): This starts from the first day of pregnancy and lasts until 12 weeks. During this stage, the formation of most of the major organs and systems takes place. The first two weeks after fertilization are called the embryonic stage, during which the main organ systems are formed. After 8 weeks, the embryo becomes a fetus. Women often experience early pregnancy symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, increased urination and breast tenderness.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-27): The second trimester is generally considered the "restful" period of pregnancy. Most of the early symptoms of pregnancy go away, and the woman's belly starts to grow and you can see that she is pregnant. During this period, the fetus grows and develops rapidly, and the mother can feel its first movements. Important ultrasounds and genetic tests are performed to assess the baby's health and development.
Third Trimester (28-40 weeks): The third trimester begins at 28 weeks and continues until delivery. During this period, the fetus continues to grow and mature, and the mother may experience some physical discomfort, such as back pain, sleep problems, and frequent urination. The approach of childbirth can cause emotional anxiety and excitement. Labor can start at any time after 37 weeks.
Pregnancy is not only a period during which a new life develops, but also a period during which a woman undergoes unique physiological and emotional changes in preparation for motherhood.
What are the signs and symptoms of pregnancy?
Every woman can experience pregnancy symptoms differently. Some women may notice signs of pregnancy as early as the first few weeks after conception, while others may experience symptoms later or be less noticeable. Here are some of the most common signs and symptoms of pregnancy:
Late menstruation: This is one of the most common signs of pregnancy. However, there are other reasons that can lead to late periods, such as stress, changes in body weight or hormonal disorders.
Breast swelling and tenderness: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause breast swelling and tenderness. These symptoms may appear in the first weeks after conception.
Nausea and vomiting: Often called "morning sickness," although it can occur at any time of the day. Nausea and vomiting can start between 2 and 8 weeks of pregnancy and last up to 16 weeks or more.
Increased urination: Hormonal changes can increase the filtration rate of the kidneys, which can increase the amount of urine, which can lead to more frequent urination.
Fatigue: An increase in progesterone hormone levels during pregnancy can cause fatigue and sleepiness.
Food cravings or food aversions: Other common pregnancy symptoms include changes in food cravings or food aversions.
Although these symptoms may indicate pregnancy, they can also be symptoms of other medical conditions. Therefore, if you think you may be pregnant, it is recommended to take a pregnancy test and see your doctor.
Antenatal Care: Important Aspects
Antenatal care is an essential part of a healthy pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby. Here are some important aspects of pregnancy care:
Regular health check-ups: It is important to visit your gynecologist regularly throughout your pregnancy. During these visits, the doctor will monitor the health of you and the baby, perform the necessary tests and ultrasounds, answer your questions and help prepare you for the birth.
Balanced diet: It is important to follow a healthy and balanced diet. You will need more protein, calcium, iron and folate. It is also important to avoid alcohol, caffeine, raw or undercooked foods, and certain types of fish, which may contain high levels of mercury.
Physical activity: Physical activity can help maintain healthy weight gain during pregnancy, reduce back pain, improve sleep quality, increase energy levels, and even improve mood. It is important to choose safe exercises during pregnancy and to consult with your doctor before starting a new exercise program.
Rest and relaxation: Fatigue is a common symptom of pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters. It is important to include enough rest and relaxation in your routine.
Avoid harmful substances: Alcohol, nicotine and drugs can cause serious health problems for you and your baby and should be avoided. It's also important to be careful with some medications and supplements—even those sold over the counter may not be safe during pregnancy.
Emotional health: Pregnancy can cause a range of emotions, from joy and happiness to anxiety and depression. It's important to accept these emotions as a normal part of pregnancy and seek help if you feel you need emotional support.
A healthy pregnancy requires conscious choices and good planning. It is important to talk to your doctor or midwife if you have any questions or concerns about pregnancy care.

Pregnancy complications are possible
Pregnancy is a magical period in a woman's life, but sometimes it can be associated with various complications. Complications can occur at any time during pregnancy and each woman may have different risk factors. Here are some of the most common pregnancy complications:
Gestational diabetes: This is a condition where a woman who has not previously had diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Most women's blood sugar levels return to normal after giving birth, but they are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later.
Preeclampsia: This is a condition that usually occurs after 20 weeks of pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can cause serious health problems for the mother and the baby if it is not diagnosed and treated in time.
Anemia: Anemia is a condition in which there are too few red blood cells in the blood or they do not work properly. This can cause fatigue and reduce the ability to fight infections.
Placentas previa: This is a condition where the placenta covers the cervix, which can cause bleeding during pregnancy and delivery. Placenta previa may require a caesarean section.
Gestational hypertension: During pregnancy, women can experience high blood pressure, which can lead to complications such as preeclampsia, fetal growth retardation, or birth complications.
Miscarriage and stillbirth: Spontaneous miscarriage is the termination of a pregnancy before 20 weeks, and stillbirth is the death of a fetus after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Because every woman's pregnancy is unique, what is a risk for one woman may not be a risk for another. It is important to keep in touch with your doctor and follow their advice to prevent or manage possible pregnancy complications.
Pregnancy is a magical period in a woman's life that requires special care and attention. It is important that a mother-to-be takes care of her own health and well-being to give herself and her baby the best start in life.
Sources of information:
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2018). Your Pregnancy and Childbirth: Month to Month. Washington, DC: ACOG.
Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2020). The Female Reproductive System.
Mayo Clinic. (2019). Symptoms of Pregnancy: What Happens Right Away.
American Academy of Family Physicians. (2019). Prenatal Care: Visits and Tests.
U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2019). Folic Acid in Diet.
National Health Service. (2020). Complications of Pregnancy.
# nėštumas






