
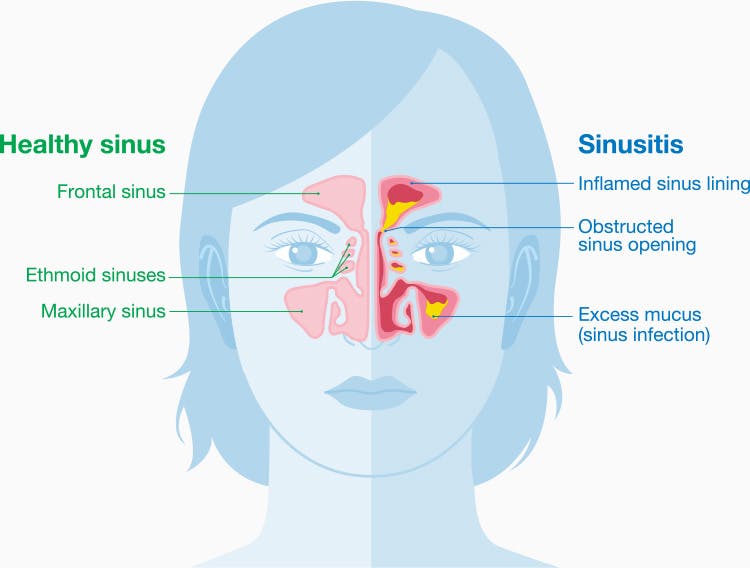
Sinusitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the nasal sinuses, the air-filled cavities in the bones of the skull around the nose. When these cavities become blocked or inflamed, it can cause sinusitis. This condition can be acute, with symptoms lasting less than 4 weeks, or chronic, with symptoms lasting more than 12 weeks. Most often, sinusitis is caused by a viral infection, but it can also be caused by bacteria or fungi.
Sinusitis can cause a variety of symptoms, such as nasal congestion or rhinorrhea (mucus), headache, facial pain or tenderness, decreased sense of smell, dry cough, or fatigue. Sinusitis is a very common condition and is usually treated by reducing symptoms and controlling the source of infection.
Causes of the disease
Sinusitis can have many causes, but most often this condition is caused by viruses or bacteria. Sinusitis can occur after a cold, flu or other upper respiratory tract infection, when the mucous membranes of the nose and throat become blocked and create a favorable environment for bacteria or viruses to spread. Fungal infections can also cause sinusitis, but this is a less common cause. In addition, structural abnormalities such as curvature of the nasal septum can also increase the risk of sinusitis.
Sinusitis is a very common condition. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 12 percent of US adults experience sinusitis at least once a year. Chronic sinusitis, with symptoms lasting 12 weeks or longer, is also a common problem that many people experience. However, despite its frequency, sinusitis is a condition that can usually be successfully managed and treated.
What symptoms indicate that you have sinusitis?
Sinusitis can cause various symptoms, which often depend on the type of disease: acute or chronic sinusitis. However, some symptoms are very common and often associated with this condition.
First, most people with sinusitis experience nasal congestion or rhinorrhea (mucus). These symptoms are caused by inflammation and fluid build-up in the sinuses, making it difficult to breathe through the nose.
Second, headache is a very common symptom of sinusitis. The pain is usually felt around the eyes, nose or temples - places where the sinuses are located. The pain may worsen when you bend over or change the position of your head suddenly.
Third, other common symptoms of sinusitis include facial pain or tenderness, decreased sense of smell, and a dry cough that may worsen at night.
In addition, some people experience fever, fatigue, or general weakness. If the sinusitis is bacterial, more severe symptoms may occur, such as a high fever, severe headache, swelling of the hands and feet, or changes in vision. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
It is important to note that the symptoms of sinusitis can be similar to those of other respiratory infections, such as the common cold or flu. Therefore, if you suspect you have sinusitis, it is important to see your doctor for a correct diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment methods
Treatment for sinusitis depends on its cause, severity, and symptoms. Most cases of acute sinusitis are caused by a viral infection, which usually resolves within 1-2 weeks. In such cases, symptomatic treatment such as pain relief, fluid intake, and rest may help relieve symptoms.
If the sinusitis is caused by a bacterial infection, a course of antibiotics may be necessary. However, it should be remembered that antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, not viral ones, so they should only be used when a bacterial infection is established.
Treatment of chronic sinusitis can be more complex and often involves a longer period of medical treatment. This may include long-term antibiotics, corticosteroid nasal sprays, immunotherapy to treat allergies, or surgery if other treatments fail.
Various home remedies can also be used to relieve the symptoms of sinusitis. These can include steam breathing, hot compresses on the face, hydration and avoiding smoking.
In all cases, if you suspect you have sinusitis, it is important to see your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Untreated sinusitis can lead to complications, so it's important to take action as soon as possible.
What complications can untreated sinusitis cause?
Sinusitis, especially if it is not properly treated, can lead to several serious complications. Here are some possible complications of sinusitis:
Spread of infection: Bacterial infection can spread from the sinuses to other areas of the skull, including the brain, eyes, and bones. It can cause rare but serious conditions such as meningitis (inflammation of the membranes in the brain), orbital cellulitis (an infection of the eye tissue) or osteomyelitis (an infection of the bones in the skull).
Sinus abscess: A sinus abscess is the formation of pus in the sinuses due to inflammation. This is a rare but serious complication that may require surgical treatment.
Sinus polyps or cysts: Long-term inflammation in the sinuses can lead to the formation of polyps (soft growths) or cysts (fluid-filled). These polyps can cause additional nasal congestion and require surgical removal.
Chronic sinusitis: If not treated properly or if it continues to recur, acute sinusitis can turn into chronic sinusitis, which can last for 12 weeks or more. Chronic sinusitis can have a significant impact on quality of life and can be more difficult to treat.
Complications from sinusitis are rare, but they can be serious. Therefore, it is important that people who suspect they have sinusitis consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Sinusitis causes long-term consequences
Sinusitis, especially chronic or untreated, can have long-term consequences for both health and quality of life. It depends on the person and their specific situation, but here are some possible consequences of sinusitis:
Persistent discomfort and symptoms: Sinusitis can cause persistent discomfort and symptoms such as facial pain, nasal congestion, and cough. This can have a negative impact on quality of life, including work ability, learning and general well-being.
Sleep disorders: Nasal congestion and difficulty breathing can cause sleep disorders, including sleep apnea. In the long run, this can lead to fatigue, reduced work capacity and other health problems.
Impaired sense of smell: Sinusitis can temporarily impair the sense of smell, which is important for the sense of taste in food.
Complications: As mentioned in the previous paragraph, sinusitis can cause serious complications, such as the spread of infection in the skull, abscesses and polyps or cysts.
Psychological consequences: A long-term medical condition such as sinusitis can cause stress and anxiety, which can have a negative impact on emotional health.
These results show that the prevention and treatment of sinusitis is important not only in terms of health, but also in terms of quality of life. Consultation with your doctor and proper treatment can help prevent many of these potential consequences.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Allergies-vs-Sinus-Infections_Illustrator_Sydney-Saporito_Final-fd354a1641c34216b3642292fb6ee1f7.jpg)
Prevention of sinusitis
Prevention of sinusitis can be divided into two main aspects: prevention of the source of inflammation and strengthening of immunity. Here are some specific tips to help reduce your risk of sinusitis:
Hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially before eating, after contact with sick people, and after using public places where infections spread more easily.
Avoiding tobacco smoke: Smoking or secondhand smoke can irritate the sinuses, increasing the risk of sinusitis.
Allergy control: If you are allergic, effective allergy control is essential to prevent inflammation and edema.
Avoiding dehydration: Drinking enough water helps keep mucus fluid and prevents sinus congestion.
Air humidification: Dry air can dry out the sinuses and cause inflammation. Humidifiers can help, especially during the winter season when the air in the home is often dry.
Regular physical activity: Physical activity can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of inflammation.
Vaccination: Seasonal flu vaccination and pneumococcal vaccine can help protect against infections that can cause sinusitis.
It is important to remember that although these tips can reduce the risk of sinusitis, they do not guarantee complete protection. If you have persistent sinus problems, it's best to talk to your doctor about possible causes and individual prevention methods.
Sources of information:
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Sinusitis. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-sinusitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351661
American Academy of Otolaryngology. (2021). Sinusitis. https://www.entnet.org/content/sinusitis
Harvard Health Publishing. (2019). Sinusitis. https://www.health.harvard.edu/a_to_z/sinusitis-a-to-z
CDC. (2018). Chronic Sinusitis. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/sinuses.html
MedlinePlus. (2021). Sinusitis. https://medlineplus.gov/sinusitis.html
American Family Physician. (2019). Sinusitis: Over-the-Counter Medicines and Home Treatment. https://familydoctor.org/condition/sinusitis/
Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2021). Chronic Sinusitis. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/chronic-sinusitis
# sinusitas # sloga






