Back pain is one of the most common health problems worldwide, affecting people of all ages. Its causes are diverse and often complex, including structural, functional, and psychosocial factors. The causes of back pain can be divided into several main categories: mechanical/degenerative, traumatic, infectious, inflammatory, and other causes.
What are the causes of back pain
Mechanical or degenerative causes
The most common causes of back pain are mechanical or degenerative changes related to muscle strain, hernias, joint wear and tear (arthrosis), disc degeneration or spondylolisthesis (displacement of vertebrae). This category also includes scoliosis (curvature of the back) and other spinal deformities. These disorders can put pressure on the nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs.
Trauma
Trauma such as falls, sports injuries, or traffic accidents can cause back pain due to soft tissue (muscle, ligament, tendon) damage, fracture, or ligament strain. Pain can occur immediately after an injury or develop over time due to chronic tension and insufficient healing.
Infections
Although less common, infections can also cause back pain. For example, osteomyelitis (bone infection), discitis (infection of the disc ring) or epidural abscess. These conditions are usually accompanied by fever and general weakness.
Inflammatory diseases
Inflammatory diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis and other seronegative spondyloarthropathies cause inflammation of the spine, resulting in pain and movement limitations. These diseases usually occur in younger adults and may be linked to genetic factors.
Other reasons
Back pain can also be caused by some systemic diseases, such as cancer that has spread to the bones, kidney disease that causes pain in the lower back, or heart disease. Psychosocial factors such as stress, depression and anxiety can also increase sensitivity to pain or cause pain to increase due to tension and muscle tension.
Diagnosing and treating back pain requires a thorough medical history, physical examination, and, if necessary, additional tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) to determine the exact cause of the pain and develop an effective treatment plan. It is important to note that many cases of back pain go away on their own or can be successfully treated with conservative measures such as rest, pain relievers, physiotherapy or exercise.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/backpainfinal-01-5c3ba0bf46e0fb0001b5b300.png)
Back pain and its treatment methods
The treatment of back pain is complex and often requires an individualized approach, depending on the cause of the pain, its severity and the patient's state of health. Treatment options range from conservative methods, such as physical therapy and medication, to invasive procedures, including surgery. The following is an overview of the various treatments for back pain.
- Physiotherapy is one of the main treatments for back pain to strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility and reduce pain. Individualized exercise programs can help patients restore range of motion, reduce stress on back tissues, and improve overall physical condition. Various physiotherapy procedures are also used, such as electrotherapy, ultrasound or heat and cold therapy, which help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Drug therapy is often used as a first aid for back pain relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be prescribed to control inflammation and pain. In more severe cases, stronger pain relievers, including opioids, may be prescribed, but are used with extreme caution due to the risk of addiction. In some cases, muscle relaxants or antidepressants may be used to help control chronic pain.
- Chiropractic and osteopathy are alternative treatment methods that involve manual adjustments to the spine and other parts of the body. These procedures aim to restore normal movement function, reduce pain and improve the patient's overall well-being. Although some studies show that these methods can be effective for certain patients, it is important to choose qualified and experienced professionals.
- Different types of injections can be used to relieve pain, including corticosteroid injections into inflamed or painful areas and nerve block injections, which help temporarily block pain signals. These procedures are performed by precisely directing materials to problem areas using image guidance techniques such as fluoroscopy.
- Surgery is usually considered a last resort when conservative treatment methods fail and the patient's quality of life is greatly reduced. The most common surgeries are discectomy (removal of part of the herniated disc), laminotomy or laminectomy (removal of part of the vertebral arch to relieve pressure on nerves), and spondylodesis (fusion of vertebrae to stabilize the spine). Indications for surgery include a hernia, severe and persistent pain that radiates to the legs, and neurological symptoms such as limb weakness or loss of control.
- Alternative treatments such as acupuncture, yoga, or meditation may also be used, which can help some patients reduce pain and improve overall well-being. These methods are often integrated into comprehensive treatment programs, along with traditional medical methods.
Doctors emphasize that the most important thing is an integrated approach to treatment, involving the patient in treatment planning and encouraging his active participation in the treatment process. Early intervention, appropriate pain management, and an individualized treatment plan are essential components of effective back pain relief.
How to prevent back pain?
Back pain prevention is an important part of healthcare to improve quality of life and avoid long-term treatment and complications. Effective prevention of back pain involves combining several strategies, including regular exercises to strengthen the back muscles, creating an ergonomic workplace, controlling weight and maintaining a healthy posture. These tips can help you reduce your risk of back pain and maintain good spinal health.
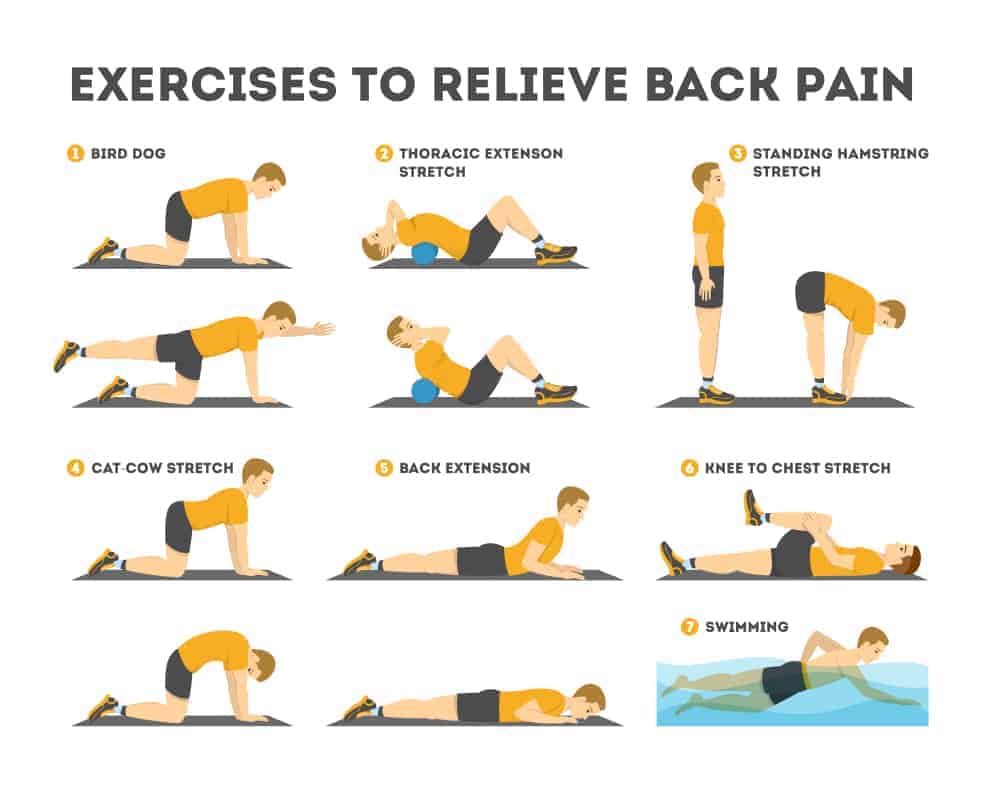
Exercises to strengthen back muscles
Regular physical exercise is essential for strengthening the back muscles and improving the flexibility of the spine. That includes:
- Abdominal press strengthening exercises that help stabilize the middle part of the body and reduce the load on the back muscles.
- Back exercises such as bridge pose and dog-bird balance that strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Stretching exercises to increase the range of motion and reduce tension in the back muscles. This includes forward bends, side bends, and standing tiptoes.
- Aerobic activities such as brisk walking, swimming or cycling can help you maintain a healthy weight and improve overall muscle tone.
Creating an ergonomic workplace
An ergonomic workplace is important to prevent back pain, especially for people who work in a sedentary position:
- The height of the chair should be adjusted so that the feet are flat on the floor.
- The desk should be at a height that allows you to keep your hands parallel to the floor when typing or using a computer mouse.
- The monitor should be at eye level so that the head and neck remain relaxed while looking straight ahead.
- Taking hourly breaks to get up, walk around, and do a few stretches are essential to reduce the strain caused by prolonged sitting.
Weight control
A healthy weight reduces pressure on the back muscles and vertebrae. Being overweight or obese increases the risk of back pain, so a healthy diet and regular physical activity are important aspects of prevention.
Healthy posture
- When standing: your feet should be shoulder-width apart, and your weight should be evenly distributed on both feet. Keep your back straight and your shoulders back.
- When sitting: keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed and your back against the backrest.
Back pain can be not only uncomfortable, but also very harmful to everyday life. Following these tips and lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of back pain and improve your overall well-being and quality of life. It's important to remember that everybody is unique, so it's important to consult your doctor or physical therapist before starting any new activities or lifestyle changes.
Information sources
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Back pain.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). (2022). Low back pain fact sheet.
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS). (2022). Low back pain.
# nugaros skausmas






