
The liver is a vitally important internal organ located in the human abdominal cavity, directly below the diaphragm on the right side. It is the largest solid organ in the body, performing numerous functions necessary for normal body operation and health. The liver acts as the main detoxification center, removing toxins from the blood, and participates in the metabolism of nutrients, protein synthesis, carbohydrate storage (e.g., in the form of glycogen), fat breakdown, and the processing of cholesterol and bilirubin. It also produces important plasma protein fractions, including coagulation factors, and plays a crucial role in the immune system's function, filtering and destroying pathogens that enter the bloodstream.
Liver health is essential for the overall health and well-being of the body. Healthy livers ensure efficient toxin removal, regulation of metabolic processes, and essential substances for blood clotting. However, despite their resilience and regenerative power, the liver can be damaged by various factors, including excessive alcohol consumption, viral infections (e.g., hepatitis), autoimmune inflammation, medications, and toxins, as well as obesity, which can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Liver health disorders can manifest as mild functional disturbances, which can be reversible with proper intervention, or serious conditions, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, which can cause long-term health damage or even death.
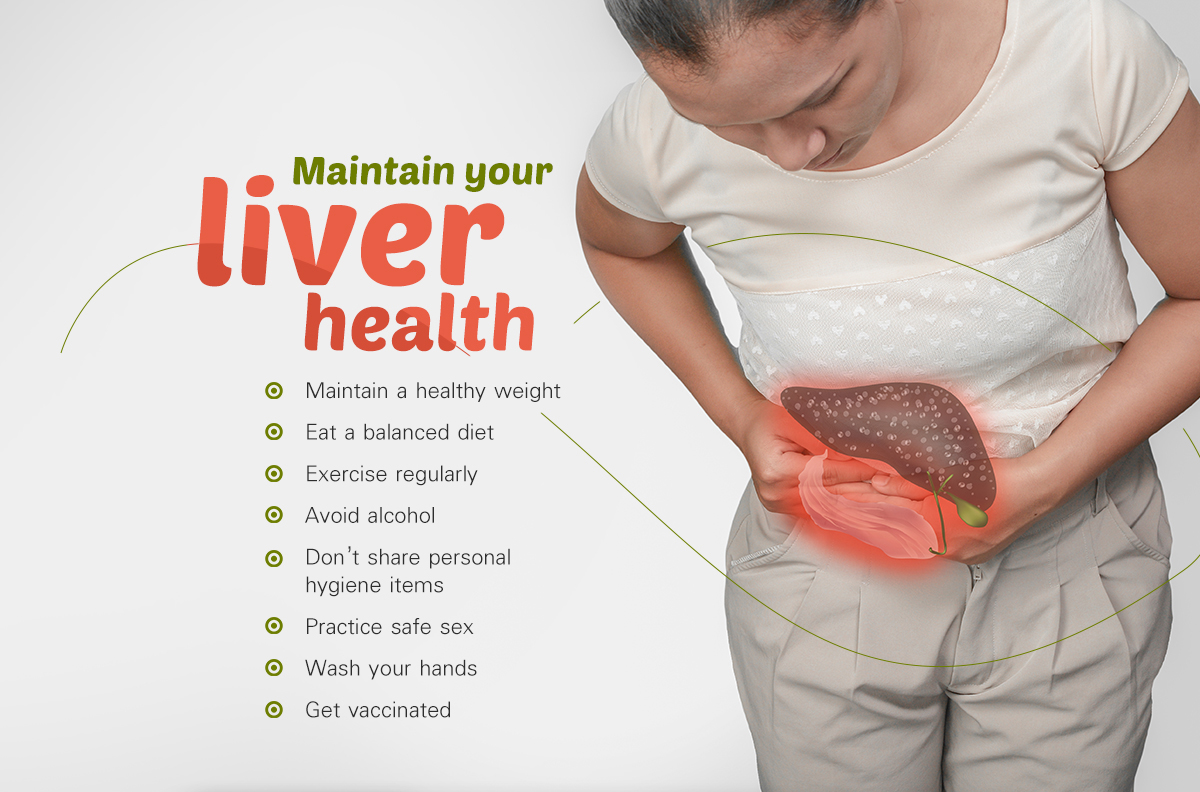
Fundamentals of liver health maintenance
The fundamentals of maintaining liver health are vitally important to ensure the efficiency of this critical organ's functions and long-term well-being. Located in the human body's abdominal cavity, the liver performs various vitally important functions, including the regulation of metabolism, removal of toxins from the blood, synthesis of essential proteins, and storage of nutrients. Healthy livers are necessary to maintain overall body health and effectively resist diseases. Key aspects of liver health maintenance include a balanced diet, adequate physical activity, weight control, limiting alcohol consumption, and cautious use of medications and other potentially liver-damaging substances.
Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins from low-fat sources is incredibly important. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flax seeds, can help reduce inflammation and improve liver function. It's also important to limit saturated fats, added sugars, and processed foods high in sodium, as these can contribute to the risk of liver diseases.
Physical activity
Regular physical activity is another important aspect of liver health. Physical activity helps control body weight, reduces fat accumulation in the liver, and promotes better insulin sensitivity. This is especially important for preventing or managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), one of the most common liver diseases. Engaging in moderate-intensity physical activity daily, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, is recommended.
Weight control
Weight control is essential, as overweight or obesity significantly increases the risk of fat accumulation in the liver, which can lead to NAFLD or even cirrhosis. Combining a healthy diet and regular physical activity is the most effective way to maintain a healthy body weight.
Limiting alcohol consumption
Limiting alcohol consumption is critically important, as excessive alcohol intake is one of the primary causes of liver diseases, including alcoholic liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Even reducing moderate consumption can have a positive impact on liver health.
Cautious use of medications
Cautious use of medications is necessary, as some drugs, especially when used in large doses or over a long period, can harm the liver. It's important to avoid overdosing on over-the-counter medications, such as paracetamol, and consult with a healthcare professional regarding the use of any drugs, including dietary supplements and herbal preparations.

Additional prevention measures for maintaining liver health
Additional prevention measures are necessary to comprehensively maintain liver health and protect this vitally important organ from diseases and damage. These measures include vaccination, regular medical checkups, avoiding toxins, maintaining healthy gut flora, and managing psychosocial health.
These preventive strategies complement the main principles of liver health maintenance, such as a balanced diet, physical activity, weight control, limiting alcohol consumption, and cautious use of medications.
- Vaccination is critically important to protect the liver from infectious diseases, such as hepatitis A and B. These vaccines are effective measures to prevent viral hepatitis, which can cause long-term liver damage and diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer. The World Health Organization (WHO) and local healthcare institutions recommend hepatitis A and B vaccination for individuals at higher risk and as part of general vaccination programs. Regular medical checkups, including liver function tests, are important for early disease diagnosis and treatment. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals and monitoring of liver condition help identify any liver function disorders or diseases at an early stage when treatment is most effective. This includes blood tests that measure various liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and other indicators of liver health.
- Avoiding toxic substances is another important area of prevention. This includes both environmental toxins, such as chemicals and heavy metals, and internal toxins resulting from improper diet or substances that can harm the liver. In the workplace, where there may be a risk to liver health due to chemicals or toxic substances, it's important to use appropriate protective measures and adhere to safety protocols.
- Maintaining healthy gut flora can also have a positive effect on liver health. Studies show that the gut microbiome and liver are closely connected through the so-called gut-liver axis, and an imbalance in gut flora can contribute to liver inflammation and diseases. Therefore, a balanced diet rich in fiber and probiotics is important for maintaining good gut health and, in turn, liver health.
- Managing psychosocial health, including stress reduction and adequate rest, is also an important aspect of liver health. Stress and excessive fatigue can have a negative impact on liver function, so it's important to find effective stress management strategies, such as meditation, yoga, regular physical activity, or a hobby that provides pleasure and relaxation.
These additional prevention measures, combined with the main principles of liver health maintenance, form a comprehensive approach to protecting and strengthening liver health, reducing the risk of diseases, and promoting overall well-being.
Maintaining liver health requires an integrated approach, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight control, limiting alcohol consumption, and protection from toxins. It's also important to have regular health checkups and get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B. Following these recommendations and relying on reliable sources can significantly reduce the risk of liver diseases and maintain liver health.
Information sources
- Mayo Clinic
- American Liver Foundation
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
# kepenų sveikata






