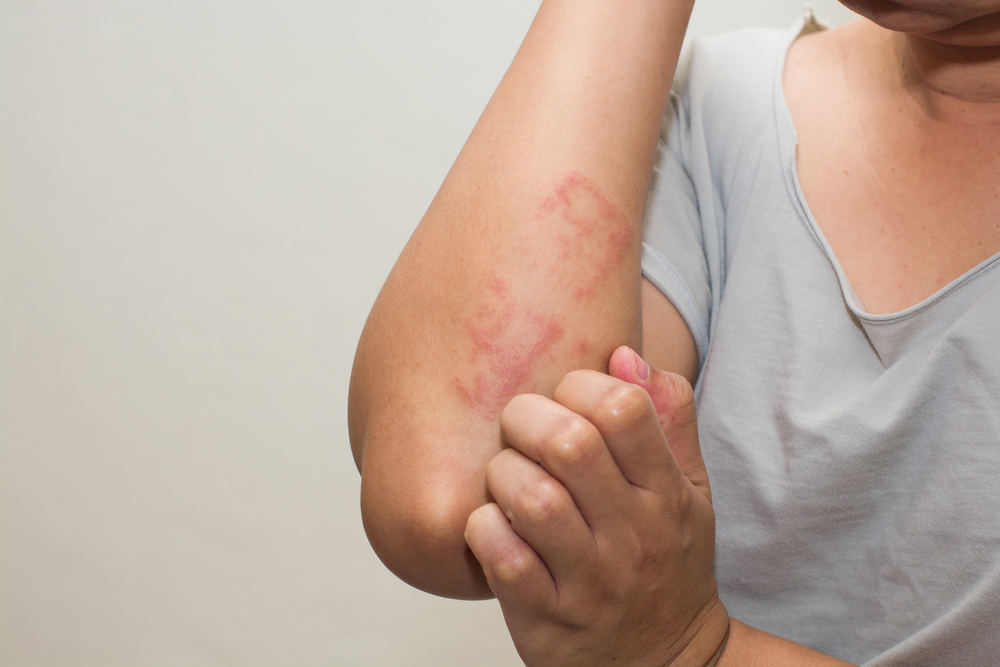
Scabies in medical terminology is a subjective skin sensation that causes the urge to scratch or rub an area of skin. Scabies can be considered a common symptom associated with a variety of skin and systemic disease conditions. Scabies can also be psychogenic or occur as a side effect of medications.
Scabies can occur locally (on a specific part of the body) or systemically (over the entire body), depending on the underlying cause. Their intensity can also vary from mild and short-term discomfort to intense and long-term suffering that can have a significant impact on quality of life.
The main mechanisms responsible for pruritus can be divided into categories: peripheral (skin), central (brain), systemic (body) and psychogenic (psychological). Each category can work alone or together, so causes and treatments can be complex. Therefore, scabies is not only an unpleasant symptom, but also a complex medical phenomenon that requires further research.
Why do scabies occur?
The causes of itching are very diverse and can be divided into several categories. The most common causes of itching are skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, contact dermatitis, allergies, dry skin, and mosquito bites. Often, these conditions cause skin irritation and inflammation, leading to scabies.
Systemic diseases can also cause itching, especially if they affect the skin or change the metabolism. For example, liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid problems, anemia, and oncological diseases such as lymphoma or leukemia can cause itching. In these situations, scabies is usually systemic rather than localized to a specific part of the body.
Neuropathic scabies occurs when disorders or damage to the nervous system cause itching. It can be caused by nerve trauma, viral infection, diabetic neuropathy, or neurological disorders.
Some medications can also cause itching as a side effect. These include antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, morphine, and some chemotherapy drugs.
Finally, scabies can be psychogenic, that is, related to psychological factors such as stress, anxiety or depression. Scabies can be difficult to manage because it is not associated with physical changes in the skin or body. These reasons show that scabies is a complex symptom, the treatment of which requires a thorough investigation.
Symptoms of itching
The main symptom of scabies is a strong desire to scratch, but often scabies occurs with other symptoms, depending on their cause.
If the itching is caused by a skin disease, other skin symptoms may occur, such as redness, swelling, peeling skin, rash, blisters, spots or cracks. Some patients may notice changes in skin color or roughness.
Systemic diseases can cause scabies without obvious skin changes. For example, liver or kidney disease may cause itching all over the body, but the skin may appear normal. In this case, there may be other systemic symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, changes in appetite, or yellow skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
Neuropathic scabies, caused by nerve damage, may be associated with a burning sensation, pain, or tingling in the affected area.
Scabies can also be associated with psychological factors such as anxiety, depression or obsessions.
It is important to mention that constant scratching or rubbing can damage the skin and cause complications such as infections, scarring or changes in pigmentation. Scabies is therefore not only a nuisance, but also a potential risk factor for skin health.
How is scabies diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pruritus begins with a detailed interview with the patient, where the doctor tries to learn about the onset, duration, intensity of symptoms, factors that increase or decrease pruritus, as well as past medical history, including skin diseases, allergies, systemic diseases and medications. The doctor may also ask about lifestyle factors, such as changes in diet, new detergents or clothing, as these may cause contact dermatitis.
A physical exam is the next step in which the doctor examines the skin in detail to identify any visible changes such as rash, blisters, redness.
Lab tests, such as blood tests, may also be done to make sure there are no systemic conditions that could be causing the pruritus.
If the pruritus is neuropathic, a neurological examination or certain nerve function tests may be necessary. If it is suspected that the scabies has a psychogenic cause, a consultation with a psychiatrist or psychologist may be useful.
Diagnosing scabies can be a challenge because there are usually many different causes of scabies. However, with a thorough examination and the use of appropriate diagnostic methods, in most cases, the main cause of itching is identified and the appropriate treatment is selected.
Treatment methods
Treatment of scabies depends on its cause. The general principle is to remove or control the underlying cause and reduce the symptoms of scabies. Various treatments include topical agents, systemic treatments, physiotherapy, psychological support and lifestyle changes.
Local preparations. These are medications that need to be applied directly to the skin where the scabies occur.
Systemic treatment. These are medications that need to be taken by mouth or injected.
Physiotherapy. This may include ultraviolet (UV) rays, in some cases using psoralens (PUVA therapy), especially for psoriasis or other skin conditions that respond to this therapy.
Psychological help. It can be beneficial for patients whose scabies are associated with psychological factors such as stress, anxiety or depression.
Lifestyle changes. This may include changes in skin care, such as gentle cleansers, moisturizing lotions, and avoiding irritants, allergens, or heat. Changing your eating habits can be helpful, especially if you have food allergies.
Although scabies can be effectively controlled in most cases, sometimes it can be a long-term and challenging process that requires individualized and integrated treatment.
Scabies is a common and sometimes difficult-to-manage symptom with a variety of causes, including skin conditions, systemic diseases, nerve damage, drug side effects, and psychological factors. Scabies can have a significant impact on patients' quality of life, causing discomfort, pain, disturbed sleep and psychological stress.
Sources of information:
Mayo Clinic.
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS).
American Academy of Dermatology Association (AAD).
WebMD.
British Association of Dermatologists (BAD).
Research Articles. Scientific article databases such as PubMed.
# niežai # odos problemos






