
Nail fungus, scientifically known as onychomycosis, is a contagious disease caused by fungi that have the ability to infect the nails. These fungi, usually dermatophytes, are microscopic organisms that like moist and warm environments, so they often colonize the nails, especially the toenails.
Nail fungus can affect any nail, but it is most common on the toenails. This distribution is due to the fact that the toenails are permanently closed, which often creates an optimal environment for the growth of fungi, namely warm, dark and moist.
Nail fungus is very common, especially among adults and the elderly. This can cause aesthetic problems, as nail fungus can change the color and texture of the nails, and can also cause discomfort and pain. In addition, long-term and unnoticed infection can cause damage to the nail plate and even its rebound from the nails.
Why is nail fungus contagious?
Nail fungus infection is usually caused by three groups of fungi: dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. Dermatophytes are the most common causative agents of nail fungus, mainly affecting the toenails.
Causes and risk factors:
Age: Nail fungus is more common in older people because their nails grow more slowly and their immune systems are weaker.
Working in a humid environment: Working in a humid environment increases the risk of nail fungus.
Public places: Swimming in public pools, using shared saunas can increase the risk.
Skin and nail injuries: Skin and nails that are damaged or weak are more vulnerable to infection.
Weakness of the immune system: A weak immune system associated with diseases such as diabetes, AIDS, or due to certain medications can increase the risk of infection.
Nail fungus is very common. Statistics show that about 10 percent of adults experience nail fungus infection during their lifetime. The incidence increases with age, and it is more common among people over 60 years of age. Also, nail fungus is more common among men than women, and among people with diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
However, despite how common nail fungus is, it is important to know that it is not inevitable. There are many ways to protect yourself from a nail fungus infection and reduce the risk of it spreading.
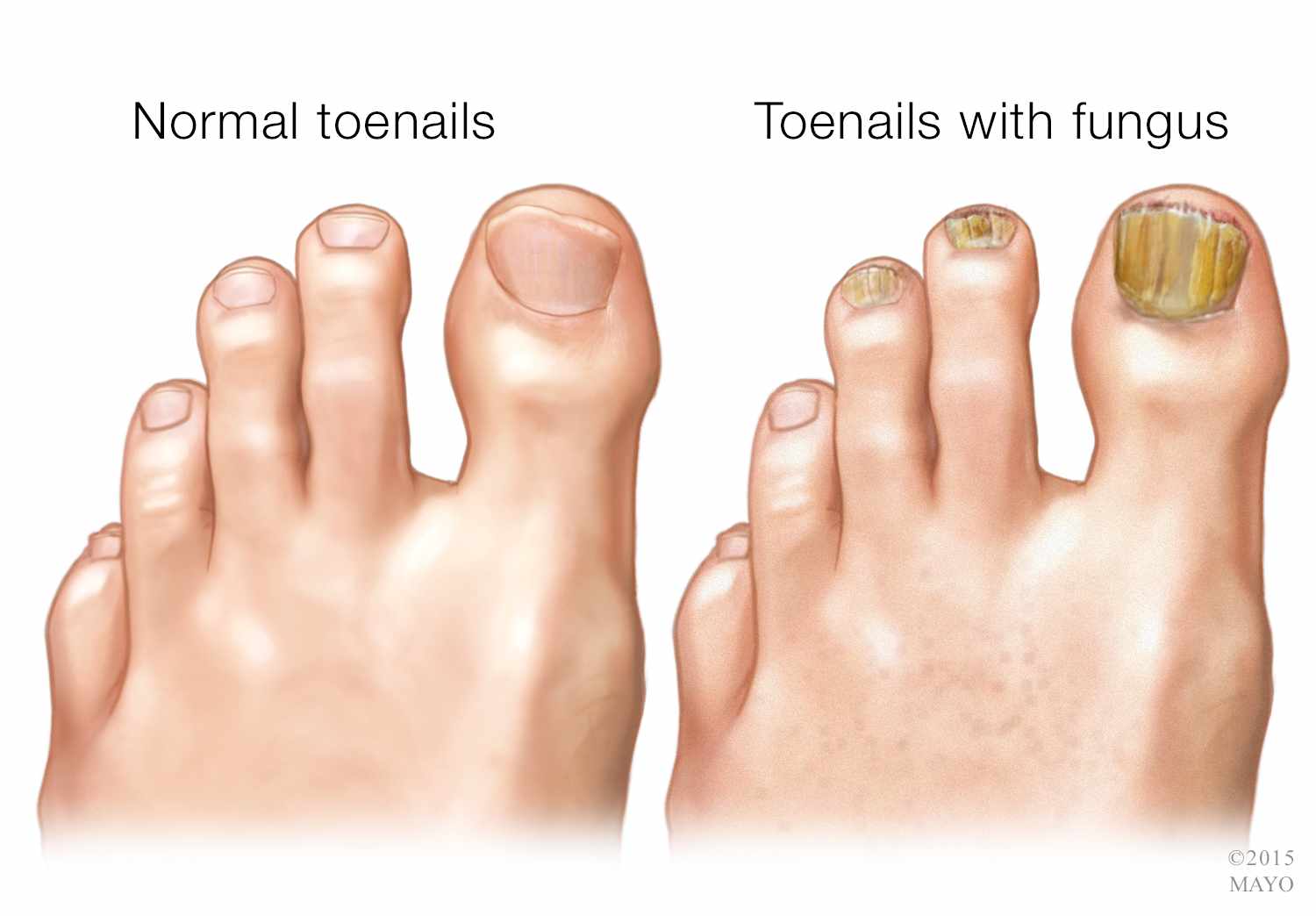
What are the signs that you have nail fungus?
Nail fungus can cause a variety of symptoms that depend on the type and degree of infection. Some people may not even know they have nail fungus, as symptoms may be mild or unnoticeable in the early stages. However, over time, without proper treatment, symptoms can worsen and become more noticeable.
Discoloration of the nail plate. One of the earliest and most common symptoms of nail fungus is nail discoloration. The fungus can cause a yellow, brown, green, white or even black color.
Thickening of the nail plate. The fungus can damage the nail plate, which makes it thicker. The thickening can cause discomfort, especially when shoes are worn.
A change in the shape of the nails. Nail fungus can change the shape of the nails, making them uneven or crooked.
Rebounding of the nail plate. The fungus can damage the nail plate, which can cause it to completely rebound and fall off. This can cause pain and discomfort.
Brittleness of nails. The fungus can damage the structure of the nails, causing them to become brittle and break easily.
Unpleasant smells. The fungus can cause an unpleasant odor from infected nails.
Redness and swelling of the skin around the nail. The fungus can cause redness and swelling of the skin around the infected nail.
It is important to know that the symptoms of nail fungus can vary from person to person, depending on the type and degree of infection, as well as on the body's individual reactions.
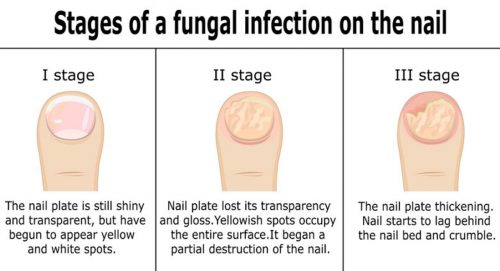
Degrees of nail fungus
The degrees of nail fungus can be divided according to the progression of the infection and the severity of the symptoms.
Primary degree. The fungus is just starting to spread and can appear as a small spot on the tip of the nail. At this stage, many people do not even suspect that they have nail fungus.
Moderate degree of difficulty. Nail fungus spreads and begins to affect larger parts of the nail. The surface of the nail may become uneven, and the color may be green, brown, or gray. The nail may begin to thicken and crack.
Difficult degree. The entire nail is affected and may appear thick, crooked and deformed. The fungus can cause discomfort or pain.
How can you prevent nail fungus?
There are various ways to reduce the risk of infection and prevent toenail fungus. Here are some tips on how to prevent nail fungus:
Personal hygiene: Regular hand and foot washing, nail trimming and brushing are some of the most important ways to prevent nail fungus. It is also important to avoid biting the nails or the skin around the nails, as this can allow the fungus to spread to the nail plate.
Wearing suitable footwear: It is recommended to wear comfortable shoes that allow air to circulate. A moist environment is ideal for the growth of fungus, so it is important to keep your feet dry.
Safety in public places: Public places such as swimming pools, saunas or gyms can be potential sources of nail fungus. In these areas, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes to protect your feet.
Use personal items: Personal items such as nail clippers, shoes, etc. sharing with other people can increase the risk of infection.
Regular nail check: It is important to check your nails regularly for any changes that may indicate an infection. Early diagnosis can help prevent the spread of nail fungus.
Healthy lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can strengthen your immune system and help protect against a variety of infections, including nail fungus.
Remember that although these tips can help reduce the risk of infection, they are not a 100% guarantee against nail fungus.
What long-term consequences and complications can nail fungus cause?
A nail fungus infection can cause many long-term consequences and complications. Here are some of them:
Changes in the nail plate: A number of physical changes can occur, such as nail deformity, thickening, discoloration (the nails may turn yellow, brown, white, or even black), nail flaking, and eventually complete nail rejection.
Pain: The infection can cause constant discomfort or pain, especially when walking or wearing shoes. This can lead to gait problems.
Psychological stress: Nail fungal infections can cause significant psychological discomfort associated with aesthetic changes. For many people, this can lead to self-doubt, anxiety and depression.
Complications with other conditions: People with diabetes who have circulatory problems may develop more serious complications, such as inflammatory skin infections or sepsis.
Spread of infection: In addition, the fungus can spread from one nail to another or from the nail plate to other parts of the body, such as the skin of the feet or even the genitals.
Lifestyle changes: An infection may require you to make changes to your normal lifestyle, such as avoiding certain activities that may increase your risk of spreading the infection.
For all these reasons, it is very important to identify and treat a nail fungus infection as early as possible to prevent long-term complications.
Sources of information:
American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Nail fungus: Diagnosis and treatment. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/nail-fungus-treatment
NHS UK. (2018). Fungal nail infection. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/fungal-nail-infection/
American Podiatric Medical Association. (n.d.). Nail Fungus. https://www.apma.org/Patients/FootHealth.cfm?ItemNumber=1523
Mayo Clinic. (2020). Nail fungus - Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nail-fungus/symptoms-causes/syc-20353294
Gupta AK, Versteeg SG, Shear NH. (2017). Onychomycosis in the 21st Century: An Update on Diagnosis, Epidemiology, and Treatment. J Cutan Med Surg. 21(6):525-539.
American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Nail fungus: How to prevent it. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/nail-fungus-prevention
# nagų grybelis # infekcija






