
A stroke is a medical condition in which part of the brain loses blood flow because a blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain is blocked (ischemic stroke) or ruptured (hemorrhagic stroke). This condition is an emergency because when brain cells are deprived of blood supply, they quickly begin to die due to lack of oxygen and nutrients.
What are the two types of stroke?
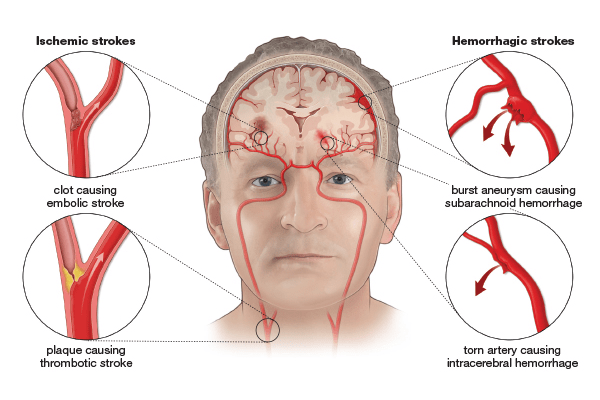
Stroke is divided into two main types depending on its cause: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, accounting for about 87% of all strokes. An ischemic stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted by a blocked blood vessel. This can happen from a blood clot (thrombus) that forms in a blood vessel in the brain, or from a clot that forms in another part of the body and travels to the brain with the blood flow.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a less common but more serious type of stroke that occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or bursts. This can happen because of a rupture of an artery on the surface of the brain or because of a rupture of a blood vessel inside the brain.
Both types of stroke are very serious and can cause long-term consequences or even death. Symptoms of a stroke can vary and depend on which part of the brain is damaged. They can include speech problems, vision problems, paralysis or weakness on one side of the body, headaches and loss of coordination. The symptoms of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke may be similar, but their treatment is different, so it is important to make the correct diagnosis as soon as possible. It is very important to seek medical attention immediately if any of these symptoms occur, as the outcome of stroke treatment can greatly depend on how quickly it is started.
Causes of stroke
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, as well as one of the leading causes of disability. This is a condition where part of the brain loses its blood supply and begins to die, causing brain damage.
The causes of stroke can vary depending on the type of stroke. Ischemic strokes are caused by the cessation of blood flow to a part of the brain due to blockage of a blood vessel. This can happen as a result of a blood clot forming in a blood vessel in the brain, or a clot that forms elsewhere in the body and travels to the brain with the blood flow (this is called an embolism).
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or bursts, causing blood to seep into the brain tissue. It can be caused by high blood pressure, trauma, blood vessel abnormalities such as aneurysms, or certain medications that interfere with blood clotting.
Stroke is the third leading cause of death and the leading cause of disability in adults in the United States. According to the World Health Organization, about 15 million people worldwide suffer a stroke every year, of which 5 million die and another 5 million leave people with long-term disability.
The risk of having a stroke increases with age, but stroke can happen to people of any age. Some factors, such as family history, race, and gender, can also increase the risk of stroke. However, many risk factors, such as high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and obesity, are controllable and can be reduced through healthy lifestyle measures and/or medications.
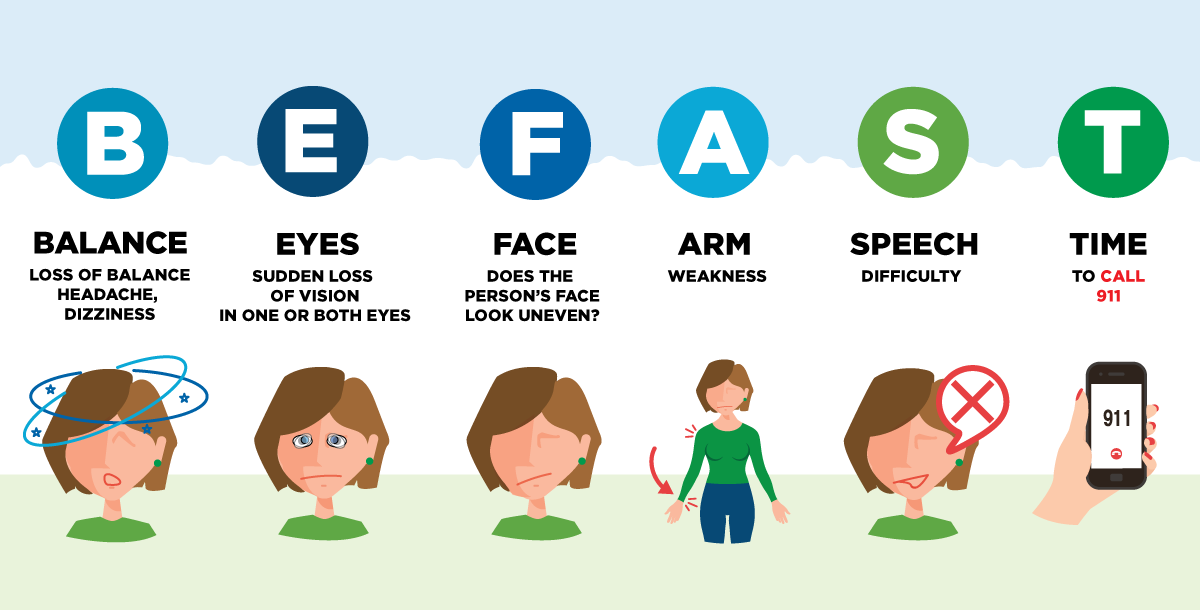
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
The symptoms of a stroke can vary greatly depending on which part of the brain is affected by the stroke. However, there are some common signs to be aware of in order to react quickly.
Distortion of the face. Often, one side of the face may become droopy or paralyzed. Some people may notice that one eye is lower or the mouth is crooked.
Weakness in arms or legs. Paralysis or weakness on one side of the body is a very common symptom of a stroke. This can manifest as an inability to raise one or both arms above the head or a leg that stops working.
Language difficulties. A stroke can cause difficulty speaking or understanding speech. This can manifest as an inability to find the right words, slurred speech.
Visual disturbances. A stroke can cause vision problems such as double vision, loss of vision in one or both eyes, or a sudden change in vision.
Headache. A stroke can cause a very severe headache that comes on suddenly and for no apparent reason.
Impaired balance or coordination. A stroke can cause sudden unsteadiness, loss of coordination or inability to walk.
Confusion or disorientation. Some people may experience disorientation, confusion or spatial disorientation.
Any of these symptoms is a medical emergency. If you suspect that you or someone else is having a stroke, call 911 immediately. The consequences of a stroke can be reduced if treatment is started as soon as possible.
What health complications can a stroke cause?
A stroke is a life-threatening condition that can cause long-term consequences and lifelong complications. Here are some possible consequences of a stroke:
Physical Consequences: A stroke can cause physical disability ranging from mild dysfunction to severe paralysis. This can include difficulty moving, walking, dressing, eating, loss of sensation or coordination, and other functions. Other physical symptoms may include facial asymmetry, speech disorders.
Cognitive effects: A stroke can have long-term effects on brain functions, including memory, attention, language comprehension, and the ability to learn. This can lead to dementia or other cognitive problems.
Emotional and psychological effects: A stroke can cause emotional and psychological problems, including depression, anxiety, mood swings, irritability, fears, etc.
Socioeconomic Consequences: Stroke can have a significant impact on a patient's quality of life, including their ability to work, perform daily activities, communicate and socialize. In addition, stroke care and treatment can be costly for the patient and their family.
It is important to note that although the effects of a stroke can be long-lasting and sometimes irreversible, many people with proper care and rehabilitation can regain some function and lead productive lives. Proper nutrition, physical activity, regular health check-ups and following your doctor's instructions can help reduce the severity of the consequences of a stroke and improve your quality of life.
Sources of information:
World Health Organization. (2019). The top 10 causes of death. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2019). Ischemic Stroke. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Ischemic-Stroke-Information-Page
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2019). Hemorrhagic Stroke. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Hemorrhagic-Stroke-Information
American Stroke Association. (2018). Stroke Symptoms. https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/stroke-symptoms
American Stroke Association. (2018). Diagnosing Stroke. https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/diagnosing-stroke
American Stroke Association. (2018). Treating Stroke. https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/treating-stroke
American Stroke Association. (2018). Preventing Stroke. https://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/preventing-stroke
# insultas
